We left last time with some questions about the working core of NE555.
Time to answer.
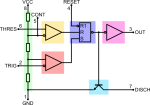
As we get a digital output from pin 3 (quite Vcc or ground) what about its generation?
We saw the input pins by which we condition the IC, particularly pins 2 (trigger) and 6 (threshold); for now leave pin 5 (voltage control) away.
We will talk about it when we'll have fixed the fundamentals inside our mind.
These two lines go directly to comparators, 2-trigger to the inverting input of the below one while 6-threshold to the non inverting of the above; and as said the comparators give high or low out signal if the voltage input difference is positive or negative respectively.
And finally, outputs to the S-R F-F (Set Reset Flip-Flop).
